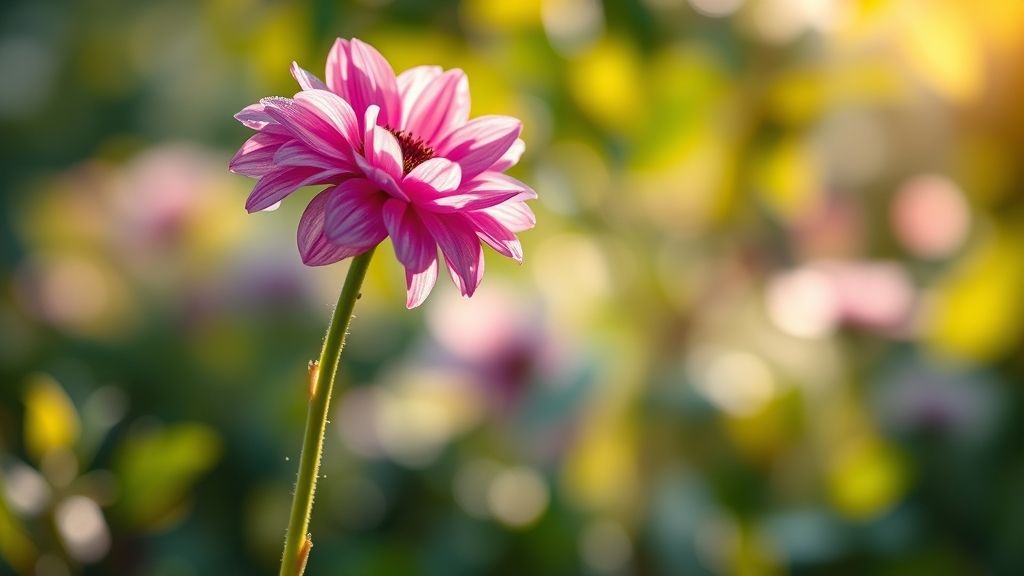
What is a Stem in a Flower?
In simple words, the stem is the part of the plant that supports the flower and connects it to the rest of the plant — especially the roots and leaves. It is usually a long, thin, green stalk that rises from the base of the plant and holds the flower above the leaves.
The stem acts as a bridge, transporting water, minerals, and food between the roots, leaves, and flowers. Without the stem, the flower would not be able to receive nutrients or stand upright.
Functions of a Flower Stem
The stem of a flower is more than just a support system. It has multiple important functions:
1. Support
The stem holds the flower upright so it can reach sunlight and be more visible to pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds. This increases the chances of pollination and reproduction.
2. Transport of Water and Nutrients
The stem contains special tubes called xylem and phloem.
- Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the flower.
- Phloem carries food (sugars made by photosynthesis) from the leaves to the rest of the plant, including the flower.
3. Growth and Development
The stem contains growth tissues called meristems. These help the stem grow taller and thicker over time, which supports the growing weight of flowers and fruits.
4. Reproduction
Some plants grow new stems from nodes (points on the stem), which can give rise to new flowers or even new plants.
Structure of a Flower Stem
A flower stem can be either herbaceous (soft and green) or woody (hard and brown). Most flowering plants, like tulips or roses, have soft, green stems.
The basic structure of a stem includes:
- Epidermis – the outer layer that protects the stem.
- Cortex – the inner layer that stores food and supports the stem.
- Vascular bundles – these include xylem and phloem tissues for transport.
- Pith – the central part of the stem that helps with storage and support.
Types of Stems in Flowering Plants
There are different types of stems in flowering plants:
1. Aerial Stems
These grow above the ground. They support leaves, flowers, and fruits. Examples include sunflower, rose, and marigold.
2. Underground Stems
Though not commonly seen, some flowers grow from underground stems like bulbs or rhizomes (e.g., tulips, lilies).
3. Climbing Stems
Some flower stems are flexible and climb with support, such as morning glories or sweet peas.
Why the Stem is Important in a Flower’s Life Cycle
Without the stem, a flower cannot grow properly. It would not be able to receive water and nutrients or maintain its structure. A weak stem means the flower could bend or break easily, affecting its ability to reproduce. For gardeners and farmers, healthy stems are essential for healthy flowers and crops.
Real-Life Examples of Flower Stems
Let’s take a look at some well-known flowers and how their stems contribute to their beauty and function:
- Roses – These have strong, woody stems that support large, heavy blooms.
- Sunflowers – Known for their tall, sturdy stems, they turn towards the sun.
- Daisies – Have long, slender stems that lift the flowers above the leaves for visibility.
- Orchids – Often have long, arching stems that support multiple flowers at once.
How to Keep Flower Stems Healthy
If you grow flowers in your garden or keep them in a vase, the health of the stem is very important. Here are some tips:
- Water regularly so that the plant can carry enough moisture to the flowers.
- Cut stems at an angle when placing in water to improve water absorption.
- Avoid damaging the stem, as wounds can block water transport.
- Support tall flowers with sticks or trellises to prevent bending or breaking.
Interesting Facts About Flower Stems
- Bamboo, one of the fastest-growing plants, is actually a type of stem!
- Some flowers like lotus have long stems that allow them to float on water surfaces.
- In cut flowers, the stem continues to absorb water for a few days, which is why keeping it in clean water is important.
Conclusion: The Power of the Flower Stem
The stem of a flower may not be as eye-catching as petals, but it is the powerhouse that keeps the entire plant alive and healthy. From providing structural support to transporting life-sustaining nutrients, the stem is the unsung hero of plant biology. Understanding the role and importance of the flower stem not only helps you appreciate nature more deeply but also helps in better gardening and plant care practices. Next time you admire a flower, take a moment to appreciate its stem — the strong, silent backbone that holds everything together.






Leave a Reply